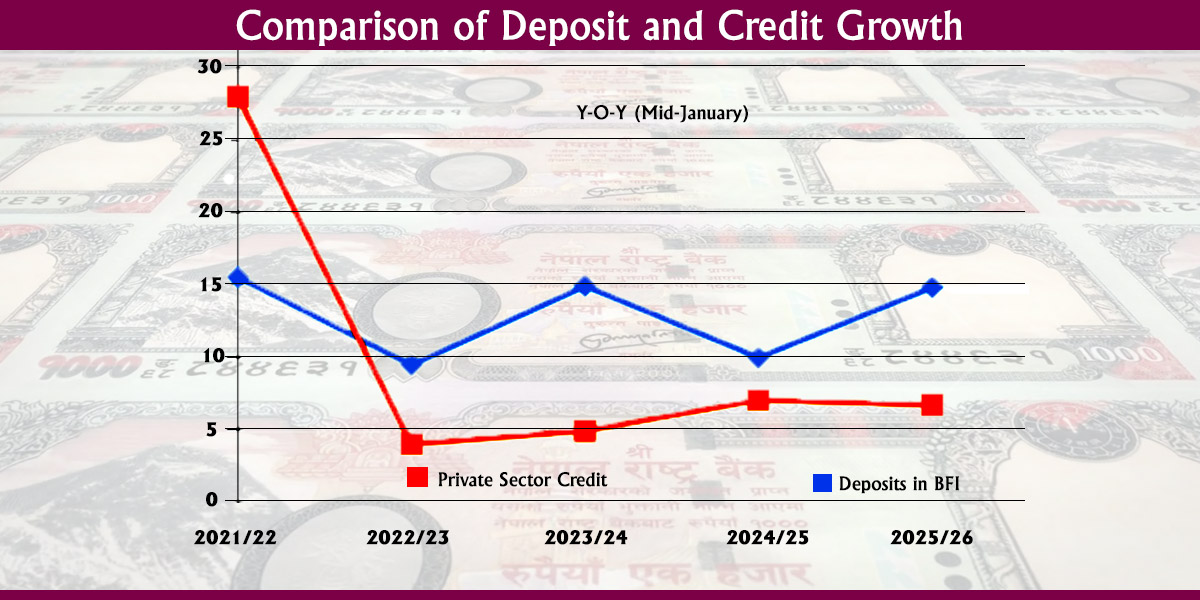
KATHMANDU: The Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) has announced plans to strengthen the oversight of large banks, which are considered crucial to the stability of the financial system.
Issuing its Monetary Policy for Fiscal Year 2025/26 on Friday, the central bank said it will identify Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) and introduce additional regulatory and supervisory measures. A separate ‘Domestic Systemically Important Bank Framework’ will be brought to enforce these provisions, it added.
Many countries have designated Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) to mitigate risks to their financial systems. These banks are identified as having a significant impact on the stability of the financial system and the broader economy. Neighboring India has designated State Bank of India (SBI), HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank as D-SIBs. While SBI and ICICI Bank were designated as D-SIBs in 2015 and 2016, and HDFC Bank was added to the list in 2017.
What Are D-SIBs?
D-SIBs are financial institutions whose size, influence and operations are so significant that their failure could severely disrupt the national economy. Commonly described as ‘too big to fail’, these banks play an essential role in maintaining payment systems, issuing credit and supporting financial stability.
The NRB’s initiative to classify and regulate D-SIBs aligns with global standards, including those outlined by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision.
Central banks all over the world designate certain banks as D-SIBs to prevent serious disruptions to the financial system if one of them experiences distress or collapses. By imposing stricter oversight on these banks, central banks strengthen their ability to withstand economic shocks. This includes requiring them to hold more capital, manage risks more effectively, and maintain detailed recovery and resolution plans.
While the NRB has yet to publish the specific directive outlining selection criteria, the process is expected to follow international models.
Typically, banks are evaluated based on their size, interconnectedness, substitutability and complexity.
Once classified as D-SIB, these banks will be subject to stricter regulations aimed at minimizing the risk of failure and reducing reliance on public bailouts. Higher capital buffers, enhanced stress testing, improved risk management, recovery and resolution planning, and closer supervision are some of the measures that D-SIBs could be subjected to.

 Himal Press
Himal Press