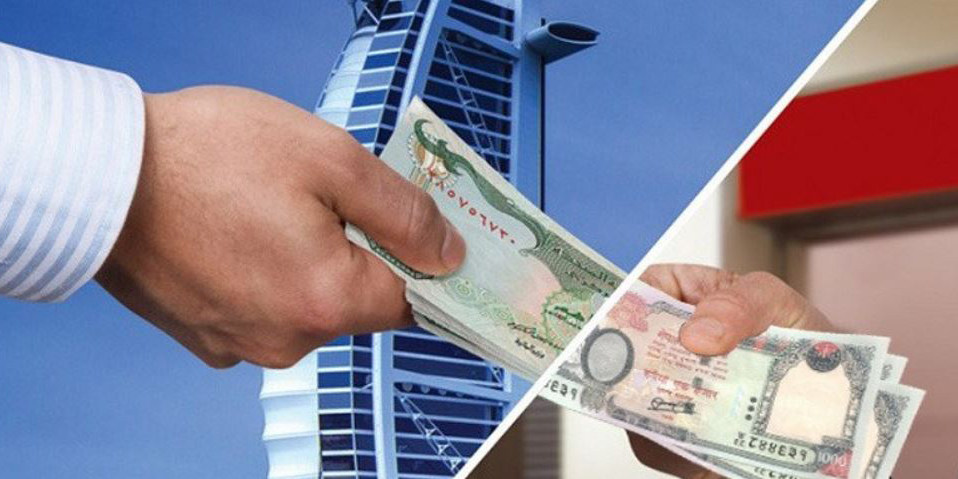
KATHMANDU: Remittance inflows surged by 21.6% to reach Rs 839 billion over the first seven months of fiscal year 2023/24.
According to the Current Macro-Economic Report for the first seven months of the current fiscal year published by the Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB), the central monetary authority, on Sunday, remittances had increased by 27.15% in the same period of the previous fiscal year. In US dollar terms, remittance inflows increased by 19.1% to 6.31 billion in US dollar terms compared to an increase of 16.4% in the same period of the previous year.
Nepali workers seeking foreign employment approval witnessed a decline in the review period, with 247,012 individuals securing first-time approvals and 158,540 renewals compared to the previous year’s figures of 314,767 and 167,708, respectively.
The current account maintained a surplus of Rs 161.69 billion in the review period. This marks a significant improvement compared to the deficit of Rs 40.16 billion in the same period of the previous fiscal year. In US dollar terms, the current account registered a surplus of 1.22 billion against a deficit of 314.6 million in the same period last year.
The current account measures the balance of trade in goods and services, net income from abroad and net current transfers. A current account surplus means that a country has more incoming payments than outgoing payments to other countries.
Likewise, the balance of payments (BOP) also showed a surplus of Rs. 297.72 billion in the review period compared to a surplus of Rs 128.55 billion in the same period of the previous year. In US Dollar terms, the BOP remained at a surplus of 2.24 billion in the review period against a surplus of 975.7 million in the same period of the previous year.
Capital transfer decreased by 29% to Rs.3.80 billion, while net foreign direct investment (FDI) remained at a positive of Rs 5.18 billion. In the same period of the previous year, capital transfer amounted to Rs 5.35 billion and net FDI amounted to Rs.1.04 billion.
Gross foreign exchange reserves increased by 19.9% to Rs 1,844.94 billion in mid-February 2024, up from Rs 1539.36 billion in mid-July 2023.
According to the report, reserves held by the NRB surged by 20.7% and reached Rs 1,623.92 billion, while reserves held by banks and financial institutions increased by 14.2% to Rs 221.02 billion in mid-February 2024 from Rs 193.59 billion in mid-July 2023.
Based on the imports of the first seven months of 2023/24, the reserves of the banking sector can cover prospective merchandise imports for 14.7 months and merchandise and services imports for 12.3 months.

 Himal Press
Himal Press