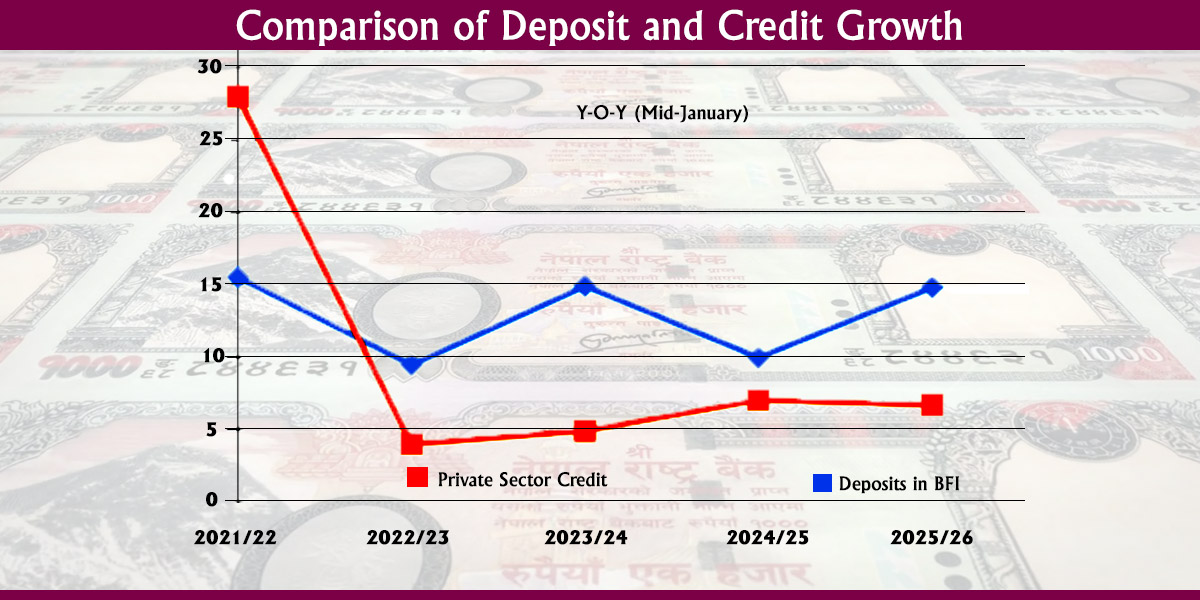
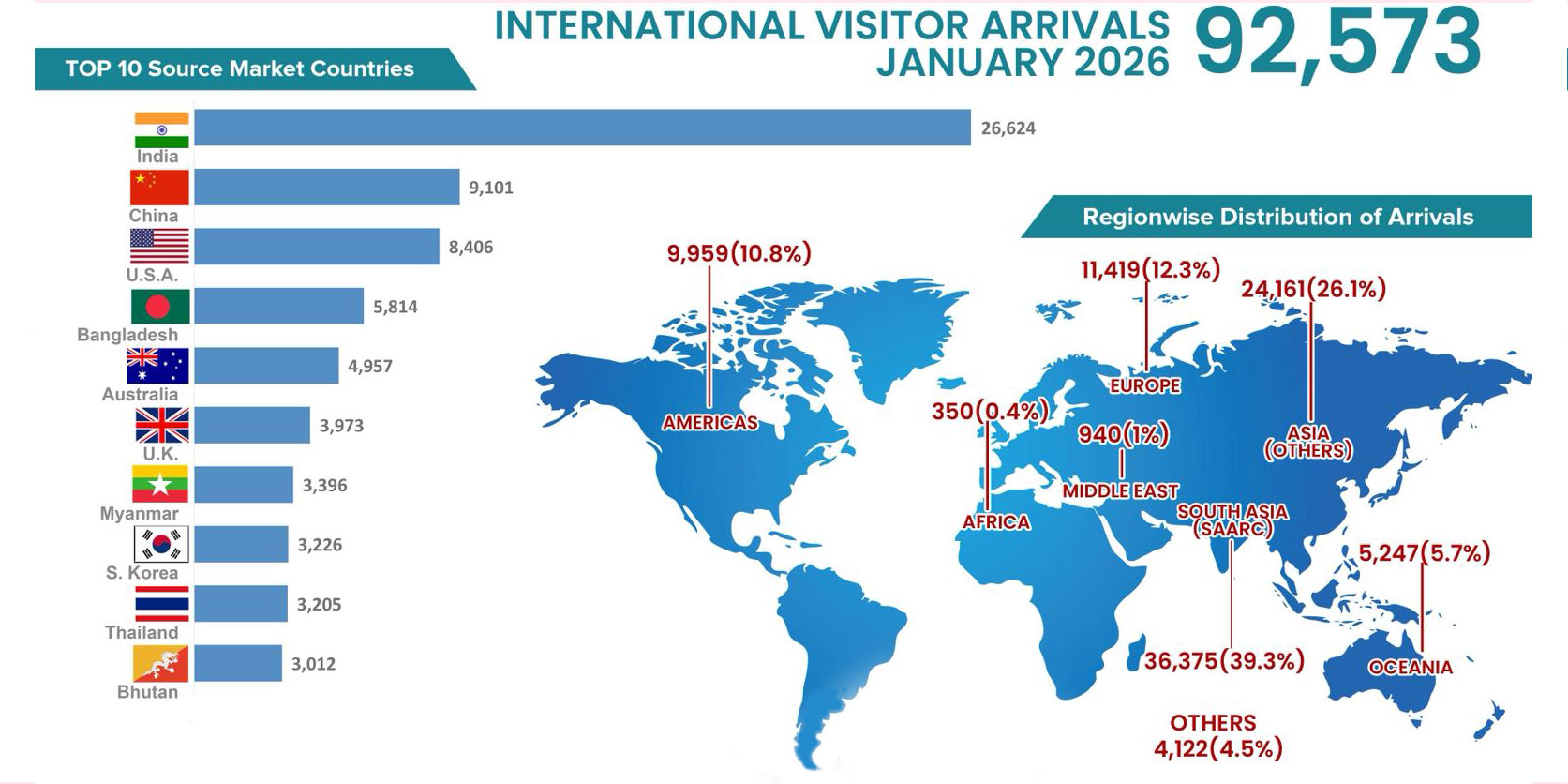
 Source: Department of Customs
Source: Department of Customs
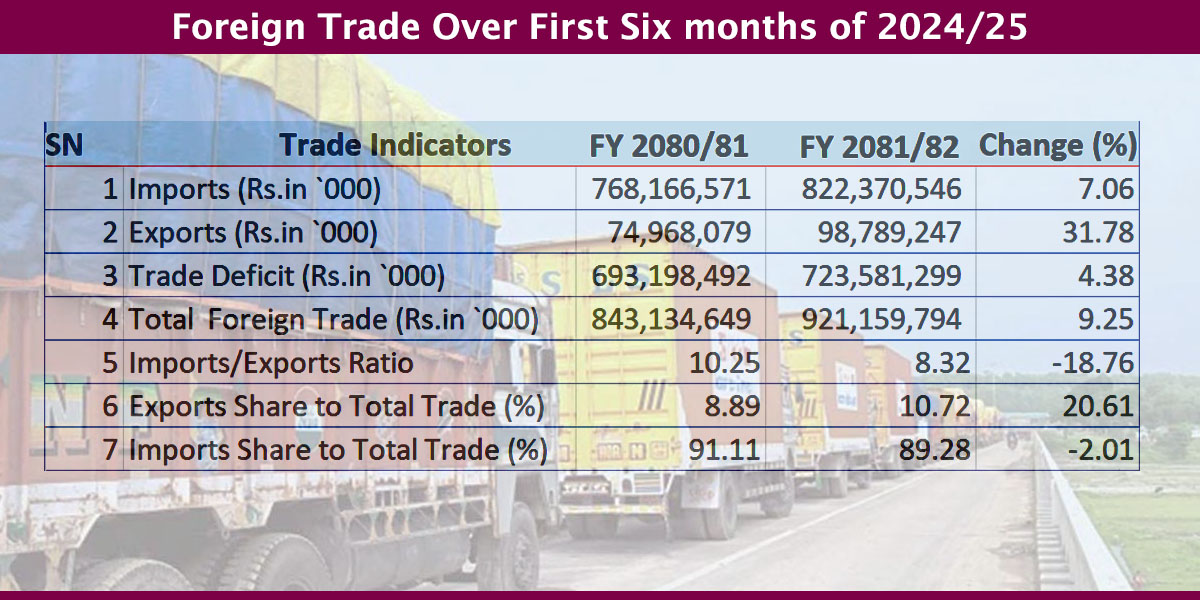
KATHMANDU: Nepal’s foreign trade grew by 9.25% to Rs 921.16 billion in the first six months of the current fiscal year 2024/25.
According to the Department of Customs (DoC), exports surged by 31.78% to Rs 98.79 billion during this period, compared to Rs 74.96 billion in the same period last fiscal year. Imports, meanwhile, rose by 7.06% to Rs 822.37 billion, up from Rs 768 billion in the first six months of 2023/24.
The country’s trade deficit widened by 4.38% to Rs 723.58 billion, up from Rs 693.19 billion in the corresponding period of the previous fiscal year.
Exports now constitute 10.72% of Nepal’s total trade, an improvement from 8.89% in the first six months of 2023/24. Meanwhile, the share of imports slightly declined to 89.28%, compared to 91.11% in the same period last fiscal year.
Petroleum products dominated Nepal’s imports. The country imported diesel, petrol, and LPG worth Rs 54.36 billion, Rs 32.14 billion, and Rs 29.79 billion, respectively. Other major imports included raw steel materials (Rs 25.71 billion) and crude soybean oil (Rs 24.37 billion).
Soybean oil, sunflower oil, big cardamom, hand-woven carpets, and tea were Nepal’s leading exports. Soybean oil accounted for Rs 18.90 billion, while sunflower oil contributed Rs 498.48 million. Exports of big cardamom, carpets, and tea stood at Rs 455.70 million, Rs 331.57 million, and Rs 280.55 million, respectively.
Nepal traded with 160 countries during the review period, enjoying a trade surplus with 33 of them. The highest surplus, Rs 463.22 million, was recorded with Afghanistan. Nepal exported goods worth Rs 475.62 million to Afghanistan and imported goods worth Rs 12.39 million.
Nepal’s largest trade deficit was with India, at Rs 439.14 billion. Imports from India amounted to Rs 502.85 billion, while exports to the southern neighbor stood at Rs 73.71 billion. Similarly, Nepal recorded a trade deficit of Rs 158.62 billion with China, importing goods worth Rs 160.54 billion and exporting Rs 1.92 billion.

 Himal Press
Himal Press